 |
Speeduino
|
 |
Speeduino
|
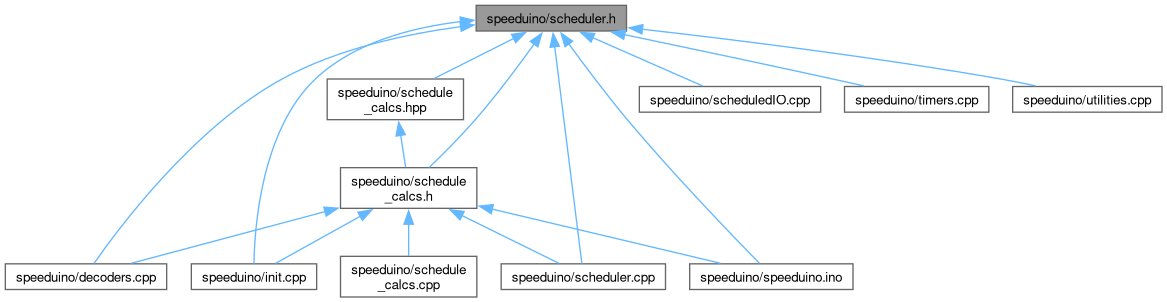
Go to the source code of this file.
Classes | |
| struct | Schedule |
| A schedule for a single output channel. More... | |
| struct | IgnitionSchedule |
| struct | FuelSchedule |
Macros | |
| #define | USE_IGN_REFRESH |
| #define | IGNITION_REFRESH_THRESHOLD 30 |
Enumerations | |
| enum | ScheduleStatus { OFF = 0b00000000U , PENDING = 0b00000001U , RUNNING = 0b00000010U , RUNNING_WITHNEXT = 0b00000100U } |
| The current state of a schedule. More... | |
Functions | |
| void | initialiseIgnitionSchedulers (void) |
| void | startIgnitionSchedulers (void) |
| void | stopIgnitionSchedulers (void) |
| void | disableIgnSchedule (uint8_t channel) |
| void | refreshIgnitionSchedule1 (unsigned long timeToEnd) |
| void | disableAllIgnSchedules (void) |
| void | initialiseFuelSchedulers (void) |
| void | startFuelSchedulers (void) |
| void | stopFuelSchedulers (void) |
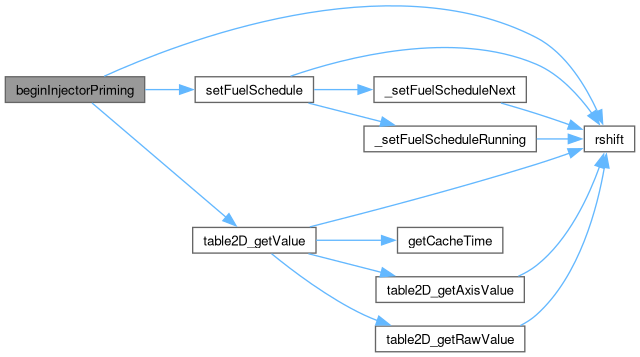
| void | beginInjectorPriming (void) |
| void | disableFuelSchedule (uint8_t channel) |
| void | disableAllFuelSchedules (void) |
| static bool | isRunning (const Schedule &schedule) |
| Is the schedule action currently running? | |
| void | setCallbacks (Schedule &schedule, voidVoidCallback pStartCallback, voidVoidCallback pEndCallback) |
| Set the schedule action start & end callbacks. | |
| void | setSchedule (Schedule &schedule, uint32_t delay, uint16_t duration, bool allowQueuedSchedule) |
| Set the schedule action to run for a certain duration in the future. | |
| void | disableSchedule (Schedule &schedule) |
| Disable the schedule. | |
| static void | setIgnitionSchedule (IgnitionSchedule &schedule, uint32_t delay, uint16_t duration) |
| Set the ignition schedule action (charge & fire a coil) to run for a certain duration in the future. | |
| void | moveToNextState (IgnitionSchedule &schedule) |
| Shared ignition schedule timer ISR implementation. Should be called by the actual ignition timer ISRs (as timed interrupts) when either the start time or the duration time are reached. See Schedule finite state machine. | |
| static void | setFuelSchedule (FuelSchedule &schedule, uint32_t delay, uint16_t duration) |
| Set the fuel schedule action (open & close an injector) to run for a certain duration in the future. | |
| void | moveToNextState (FuelSchedule &schedule) |
| Shared fuel schedule timer ISR implementation. Should be called by the actual timer ISRs (as timed interrupts) when either the start time or the duration time are reached. See Schedule finite state machine. | |
Injector and Ignition (on/off) scheduling (structs).
This scheduler is designed to maintain 2 schedules for use by the fuel and ignition systems. It functions by waiting for the overflow vectors from each of the timers in use to overflow, which triggers an interrupt.
Currently I am prescaling the 16-bit timers to 256 for injection and 64 for ignition. This means that the counter increments every 16us (injection) / 4uS (ignition) and will overflow every 1048576uS.
Max Period = (Prescale)*(1/Frequency)*(2^17)
For more details see https://playground.arduino.cc/Code/Timer1/ (OLD: http://playground.arduino.cc/code/timer1 ). This means that the precision of the scheduler is:
This differs from most other schedulers in that its calls are non-recurring (ie when you schedule an event at a certain time and once it has occurred, it will not reoccur unless you explicitly ask/re-register for it). Each timer can have only 1 callback associated with it at any given time. If you call the setCallback function a 2nd time, the original schedule will be overwritten and not occur.
Arduino timers usage for injection and ignition schedules:
Timers 3,4 and 5 are 16-bit timers (ie count to 65536). See page 136 of the processors datasheet: http://www.atmel.com/Images/doc2549.pdf .
256 prescale gives tick every 16uS. 256 prescale gives overflow every 1048576uS (This means maximum wait time is 1.0485 seconds).
| #define IGNITION_REFRESH_THRESHOLD 30 |
| #define USE_IGN_REFRESH |
Perform the injector priming pulses. Set these to run at an arbitrary time in the future (100us). The prime pulse value is in ms*10, so need to multiple by 100 to get to uS
< The number of crank degrees until cylinder 1 is at TDC (This is obviously 0 for virtually ALL engines, but there's some weird ones)
< The number of crank degrees until cylinder 2 (and 5/6/7/8) is at TDC
< The number of crank degrees until cylinder 3 (and 5/6/7/8) is at TDC
< The number of crank degrees until cylinder 4 (and 5/6/7/8) is at TDC

< The number of crank degrees until cylinder 1 is at TDC (This is obviously 0 for virtually ALL engines, but there's some weird ones)
< The number of crank degrees until cylinder 2 (and 5/6/7/8) is at TDC
< The number of crank degrees until cylinder 2 (and 5/6/7/8) is at TDC
< The number of crank degrees until cylinder 2 (and 5/6/7/8) is at TDC

Is the schedule action currently running?


| void setCallbacks | ( | Schedule & | schedule, |
| voidVoidCallback | pStartCallback, | ||
| voidVoidCallback | pEndCallback | ||
| ) |
Set the schedule action start & end callbacks.
| schedule | Schedule to modify |
| pStartCallback | Start callback |
| pEndCallback | End callback |

|
inlinestatic |
Set the fuel schedule action (open & close an injector) to run for a certain duration in the future.
| schedule | Schedule to modify |
| delay | Delay until the injector opens (µS) |
| duration | Injector open time (µS) |

|
inlinestatic |
Set the ignition schedule action (charge & fire a coil) to run for a certain duration in the future.
| schedule | Schedule to modify |
| delay | Delay until the coil begins charging (µS) |
| duration | Dwell time (µS) |
| void setSchedule | ( | Schedule & | schedule, |
| uint32_t | delay, | ||
| uint16_t | duration, | ||
| bool | allowQueuedSchedule | ||
| ) |
Set the schedule action to run for a certain duration in the future.
| schedule | Schedule to modify |
| delay | Delay until the action starts (µS) |
| duration | Action duration (µS) |
| allowQueuedSchedule | true to allow a schedule to be queued up if one is currently running; false otherwise |


|
extern |
|
extern |
|
extern |
|
extern |
|
extern |
|
extern |
|
extern |
|
extern |
|
extern |